“机器学习”系列之Logistic Regression (逻辑回归)
时间:2025-07-24 | 作者: | 阅读:0本文介绍逻辑回归,这是一种分类算法。它通过Sigmoid函数将线性回归结果映射到[0,1],以概率形式分类。损失函数为对数似然函数,用随机梯度下降或牛顿法优化。其优势在于输出概率、可解释性强等,应用于CTR预估等场景。还展示了自定义函数及调用sklearn的实现代码与结果。
“机器学习”系列之Logistic Regression (逻辑回归)
0 概念
- 逻辑回归是用来做分类算法的,大家都熟悉线性回归,一般形式是Y=aX+b,y的取值范围是[-∞, +∞],有这么多取值,怎么进行分类呢?不用担心,伟大的数学家已经为我们找到了一个方法。也就是把Y的结果带入一个非线性变换的Sigmoid函数中,即可得到[0,1]之间取值范围的数S,S可以把它看成是一个概率值,如果我们设置概率阈值为0.5,那么S大于0.5可以看成是正样本,小于0.5看成是负样本,就可以进行分类了。
1 Sigmoid激活函数
- sigmoid函数是一个s形曲线,就像是阶跃函数的温和版,阶跃函数在0和1之间是突然的起跳,而sigmoid有个平滑的过渡。
- 如下代码块运行图
- 从图形上看,sigmoid曲线就像是被掰弯捋平后的线性回归直线,将取值范围(?∞,+∞)映射到(0,1) 之间,更适宜表示预测的概率,即事件发生的“可能性” 。
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.arange(-5.0 , 5.0 , 0.02)y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))plt.xlabel('x')plt.ylabel('y = Sigmoid(x)')plt.title('Sigmoid')plt.plot(x , y)plt.show()登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
<Figure size 432x288 with 1 Axes>登录后复制登录后复制登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
2 损失函数
- 逻辑回归的损失函数是 log loss,即对数似然函数,如下
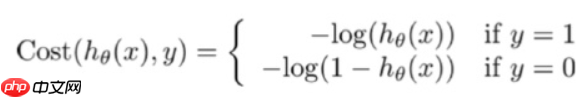
- 公式中的 y=1 表示的是真实值为1时用第一个公式,真实 y=0 用第二个公式计算损失。当真实样本为1是,但h=0概率,那么log0=∞,这就对模型最大的惩罚力度;当h=1时,那么log1=0,相当于没有惩罚,也就是没有损失,达到最优结果。所以数学家就想出了用log函数来表示损失函数。
3 优化
3.1 随机梯度下降
- 随机梯度下降J(w) 对 w 的一阶导数来找下降方向,并且以迭代的方式来更新参数
- 每次更新参数后,可以通过比较阈值或者到达最大迭代次数来停止迭代。
3.2 牛顿法
- 牛顿法的基本思路是,在现有极小点估计值的附近对 f(x) 做二阶泰勒展开,进而找到极小点的下一个估计值。
4 优势
- LR能以概率的形式输出结果,而非只是0,1判定。
- LR的可解释性强,可控度高。
- 训练快,feature engineering之后效果赞。
- 因为结果是概率,可以做ranking model。
5 应用
- CTR预估/推荐系统的learning to rank/各种分类场景。
- 某搜索引擎厂的广告CTR预估基线版是LR。
- 某电商搜索排序/广告CTR预估基线版是LR。
- 某电商的购物搭配推荐用了大量LR。
- 某现在一天广告赚1000w+的新闻app排序基线是LR。
6 自定义函数代码实现
In [1]from math import expimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inlinefrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split登录后复制 ? ?
6.1 自定义数据
In [2]# datadef create_data(): iris = load_iris() df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names) df['label'] = iris.target df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label'] data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0,1,-1]]) # print(data) return data[:,:2], data[:,-1]登录后复制 ? ?In [3]
X, y = create_data()X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)登录后复制 ? ?In [8]
import math登录后复制 ? ?
6.2 自定义逻辑回归函数
In [202]class LogisticReressionClassifier: def __init__(self, max_iter=200, learning_rate=0.02): self.max_iter = max_iter self.learning_rate = learning_rate # sigmoid激活函数 def sigmoid(self, x): return 1 / (1 + exp(-x)) def data_matrix(self, X): data_mat = [] for d in X: data_mat.append([1.0, *d]) return data_mat def fit(self, X, y): # label = np.mat(y) data_mat = self.data_matrix(X) # m*n self.weights = np.zeros((len(data_mat[0]),1), dtype=np.float32) for iter_ in range(self.max_iter): for i in range(len(X)): result = self.sigmoid(np.dot(data_mat[i], self.weights)) error = y[i] - result self.weights += self.learning_rate * error * np.transpose([data_mat[i]]) print('LogisticRegression Model(learning_rate={},max_iter={})'.format(self.learning_rate, self.max_iter)) # def f(self, x): # return -(self.weights[0] + self.weights[1] * x) / self.weights[2] def score(self, X_test, y_test): right = 0 X_test = self.data_matrix(X_test) for x, y in zip(X_test, y_test): result = np.dot(x, self.weights) if (result > 0 and y == 1) or (result < 0 and y == 0): right += 1 return right / len(X_test)登录后复制 ? ?
6.3 训练
In [203]lr_clf = LogisticReressionClassifier()lr_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
LogisticRegression Model(learning_rate=0.02,max_iter=200)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
6.4 结果展示及可视化
In [204]lr_clf.score(X_test, y_test)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
0.9666666666666667登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?In [205]
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)y_ = -(lr_clf.weights[1]*x_ponits + lr_clf.weights[0])/lr_clf.weights[2]plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)#lr_clf.show_graph()plt.scatter(X[:50,0],X[:50,1], label='0')plt.scatter(X[50:,0],X[50:,1], label='1')plt.legend()登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f232f7e6590>登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
<Figure size 432x288 with 1 Axes>登录后复制登录后复制登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
7 调用sklearn实现
- sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression参数
solver参数决定了我们对逻辑回归损失函数的优化方法,有四种算法可以选择,分别是:
- a) liblinear:使用了开源的liblinear库实现,内部使用了坐标轴下降法来迭代优化损失函数。
- b) lbfgs:拟牛顿法的一种,利用损失函数二阶导数矩阵即海森矩阵来迭代优化损失函数。
- c) newton-cg:也是牛顿法家族的一种,利用损失函数二阶导数矩阵即海森矩阵来迭代优化损失函数。
- d) sag:即随机平均梯度下降,是梯度下降法的变种,和普通梯度下降法的区别是每次迭代仅仅用一部分的样本来计算梯度,适合于样本数据多的时候。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression登录后复制 ? ?In [9]
clf = LogisticRegression(max_iter=200)登录后复制 ? ?In [10]
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, l1_ratio=None, max_iter=200, multi_class='auto', n_jobs=None, penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', tol=0.0001, verbose=0, warm_start=False)登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?In [11]
clf.score(X_test, y_test)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
1.0登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?In [12]
print(clf.coef_, clf.intercept_)登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
[[ 2.69741404 -2.61019199]] [-6.44843344]登录后复制 ? ? ? ?In [13]
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)y_ = -(clf.coef_[0][0]*x_ponits + clf.intercept_)/clf.coef_[0][1]plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)plt.plot(X[:50, 0], X[:50, 1], 'bo', color='blue', label='0')plt.plot(X[50:, 0], X[50:, 1], 'bo', color='orange', label='1')plt.xlabel('sepal length')plt.ylabel('sepal width')plt.legend()登录后复制 ? ? ? ?
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1d10e65dd0>登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
<Figure size 432x288 with 1 Axes>登录后复制登录后复制登录后复制 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
来源:https://www.php.cn/faq/1425370.html
免责声明:文中图文均来自网络,如有侵权请联系删除,心愿游戏发布此文仅为传递信息,不代表心愿游戏认同其观点或证实其描述。
相关文章
更多-

- nef 格式图片降噪处理用什么工具 效果如何
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- 邮箱长时间未登录被注销了能恢复吗?
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- Outlook收件箱邮件不同步怎么办?
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- 为什么客户端收邮件总是延迟?
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- 一英寸在磁带宽度中是多少 老式设备规格
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- 大卡和年龄的关系 不同年龄段热量需求
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- jif 格式是 gif 的变体吗 现在还常用吗
- 时间:2025-07-29
-

- hdr 格式图片在显示器上能完全显示吗 普通显示器有局限吗
- 时间:2025-07-29
大家都在玩
大家都在看
更多-
- UltraEdit怎么设置自动转换到DOS格式
- 时间:2025-10-13
-
- UltraEdit怎么关闭整字匹配
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 三角洲行动简单又好听游戏网名
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 抖音定时发布怎么取消?发布作品正确方法是什么?
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 小红书怎么注册新的账号?它起号运营怎么做?
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 快手评论被删除的原因怎么查?评论被删除有哪些原因?
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 不让别人看抖音收藏的音乐怎么弄?收藏的音乐在哪里找到?
- 时间:2025-10-13
-

- 小红书企业号认证流程是什么?企业号认证的条件是什么?
- 时间:2025-10-13








